The passage of the generation of refrigerant fluids has details that are worth mentioning and that are highlighted in the following article.
passage of the generation of refrigerant fluids has details that are worth mentioning and that are highlighted in the following article.
Ing. Ernesto Sanguinetti Remusgo*
Consequently with the evolution of refrigerant fluids, in the initial part of this article we present the first three generations of these. We continue now to develop the fourth generation.
The fourth generation of refrigerants is the result of the search for those that do not produce "Global Warming" or "Increased Greenhouse Effect". The use of inorganic refrigerants such as Ammonia (R-717) and Carbon Dioxide (R-744) that are of the first generation, flammable refrigerants such as hydrocarbons (HC), new pure substances and especially new refrigerant mixtures is encouraged. We show some of this new generation:
- Propane C3H8 or R-290, for domestic refrigeration
- Isobutane CH (CH3)3 or R-600a, for domestic refrigeration
- Propylene C3H6 or R-1270
- Tetrafluoropropylene C3H2F4 or R-1234yf, R-1234ze, R-1234zd
- Mixture of 41.5%R-32 + 10%R-152a + 48.5%R-1234ze ( R-444B)
- Mixture of 24.3%R-32 + 24.7%R-125 + 25.3%R-134a + 27.5%R-1234yf (R-449A)
- 42%R-134a + 58% R-1234ze Blend (R-450A)
- Mixture of 11% R-32 + 59%R-125 + 30%R-1234yf (R-452A)
- Mixture of 44% R-134a + 56% R-1234yf (R-513A)
Within this new generation of refrigerants you can see R-1234 with its various isomers (change of position of the atoms that make up its molecule) using to differentiate them the subfixes yf, ze, zd. They are obtained from propylene (C3H6) or (R-1270) by replacing some of their hydrogen atoms with fluorine atoms. These refrigerants are also known as Hydrofluoro Olefins (HFO) and are used as a pure substance or as a mixture of HFO with HFC (in the previous paragraph some mixtures are appreciated) and as an example we show the chemical structure of their molecules:
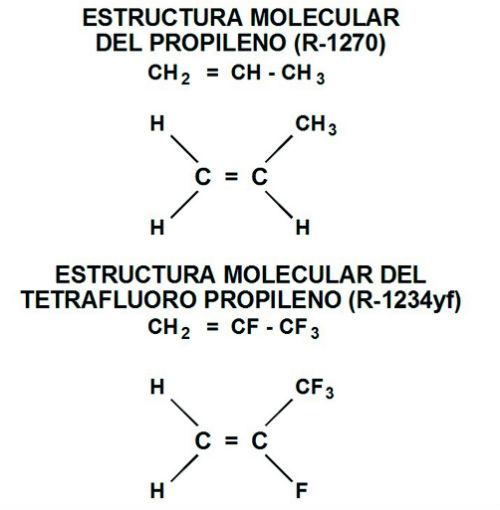
Figure 1.
As an explanation for the appearance of this fourth generation of refrigerants we will say the following:
The so-called "greenhouse effect" is the process by which the absorption and emission of thermal radiation (mainly infrared) by the gases that make up the atmosphere of our planet heat and heat the earth's surface. The behavior of the atmosphere began to be analyzed many years ago (Svante Arrhenius in 1896) and it was in 1960 that a scientist (Guy Stewart Callendar) drew attention to an abnormal increase in the average temperature of the atmosphere.
Without the atmosphere, the temperature across almost the entire surface of the earth would be below zero degrees Celsius. The atmosphere allows solar thermal radiation to pass to the surface of the earth and also allows thermal radiation to leave from the surface of the earth to the universe, managing to maintain a balance so that the temperature varies very little according to the geographical location and according to the seasons of the year, thus providing the living conditions to which we humans and all the flora and fauna are accustomed.
But when there is an imbalance, the increase in the average temperature will begin outside the usual limits and that imbalance begins when gases appear in greater proportion than normal, in the atmosphere, which do not let thermal radiation out into the universe in the normal amount, producing "atmospheric warming or global warming". The main gases of the normal greenhouse effect are water vapor (major contributor); carbon dioxide (CO2, 9 to 26%), methane (CH4, 4 to 9%) and ozone (O3, approx.7%).
Human activity since the time of the Industrial Revolution (late eighteenth century) has increased the amount of greenhouse gases in the atmosphere, leading to an increase in CO2, methane, ozone, CFCs and nitrous oxide. According to a study published in 2007, CO2 and methane concentrations have increased by 36% and 148%, respectively, from 1750 levels.
The use of fossil fuels has produced about three-quarters of the increase in CO2 from human activity over the past 20 years. The rest of this increase is mainly due to changes in land use, especially deforestation.
Just as in 1987 the UN convened a meeting of countries to sign the Montreal Protocol to give measures to protect the Ozone Layer; He also convened the Kyoto Protocol which is a protocol to the United Nations Framework Convention on Climate Change (UNFCCC) that aims to reduce greenhouse gas emissions that cause global warming: carbon dioxide (CO2), methane (CH4), nitrous oxide (N2O), hydrofluorocarbon (HFC), perfluorocarbon (PFC) and sulfur hexafluoride (SF6) gases . It was proposed to reduce by approximately 5 % within the period from 2008 to 2012, compared to emissions in 1990.
This protocol was initially adopted on 11 December 1997 in Kyoto, Japan; but did not enter into force until 16 February 2005. In November 2009, 187 countries ratified the protocol. It should be noted that some countries that are the largest contributors to this effect did not ratify the protocol.
However, the Lima Climate Summit or COP 20 Conference of the Parties held between December 1 and 12, 2014 in Lima- Peru allowed progress towards a climate agreement that involves all the countries of the world, in the next COP. Thus, with the participation of 195 countries, in the COP 21, held in Paris -France between November 30 and December 11, 2015 have finally come to agree to reduce emissions in a historic agreement to seek to safeguard the environment and keep global warming below 2 ° C by cutting carbon emissions. All participating countries committed.
Effects of climate change
The effects of climate change are being detected around the world. We will only cite some cases as an example:
Health impacts include the direct effects of extreme weather events, resulting in injuries and loss of human life, as well as indirect effects, such as malnutrition caused by crop failures due to those floods and the emergence of pests.
In the Netherlands, small islands and large deltas, as a result of the rise in sea level as the glacials of the poles melt, floods are forecast that threaten the infrastructure of the cities and even the disappearance of territories.
Finally, in order to appreciate everything mentioned about the generations of refrigerants, we present a table where the behavior of these fluids with respect to the ozone layer (ODP = Ozone Depletion Potential or Ozone Destruction Potential) and the effect on the warming of the atmosphere (GWP = Global Warming Potential = Global Warming Potential ) is observed.
It is taken as the basis of comparison of the ODP to the refrigerant R-12, with ODP = 1 and as a basis of comparison of the GWP to the R-744 (Carbon dioxide), with GWP = 1
The values that appear in the table vary somewhat according to the source of information used.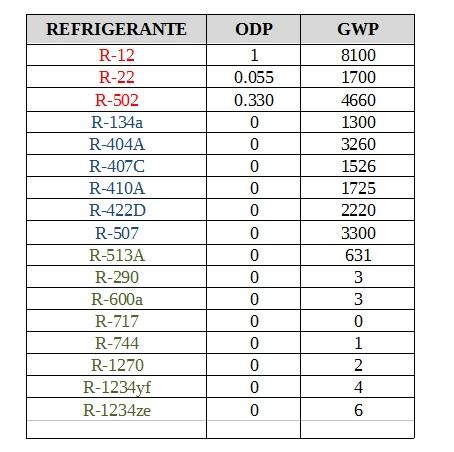
* Engineer Ernesto Sanguinetti, Engineering Division Manager of Cold Import S.A. – Lima – Peru.














