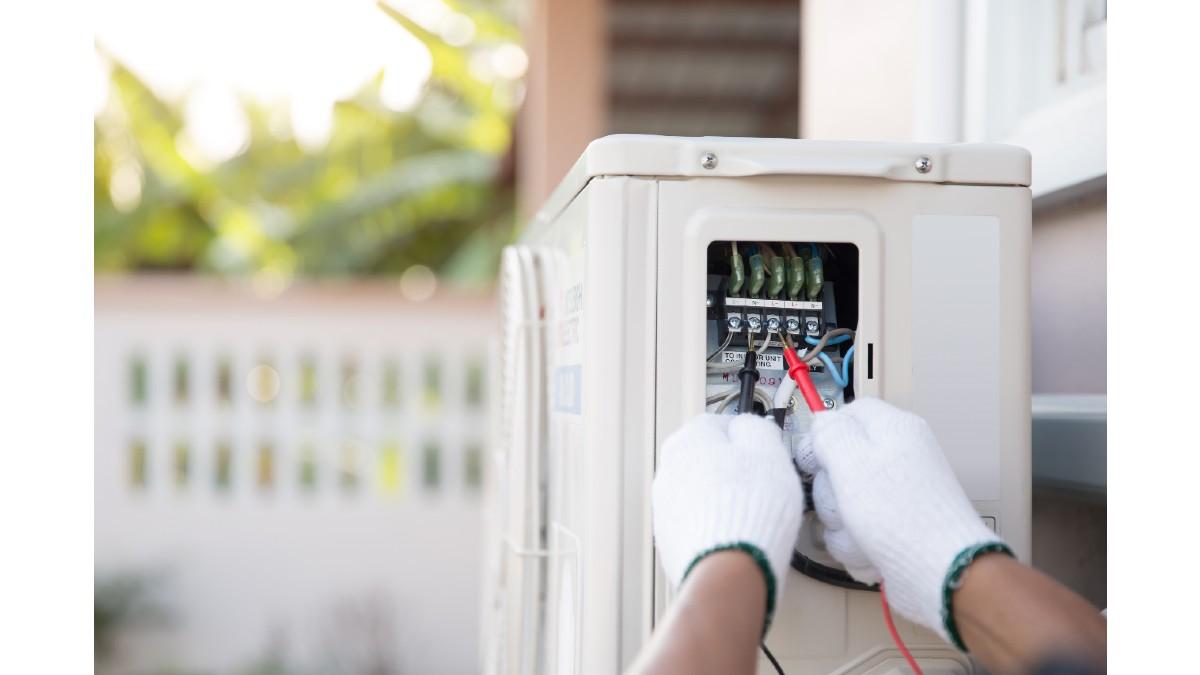
We present an alternative of cooling or heating by means of a small domestic model.
by Jimy Danelli*
As a lover of refrigeration and air conditioning with all the environmental considerations that our systems generate, such as greenhouse gases, on the one hand, and the carbon footprint left by the use of these electromechanical equipment; doing a few small exercises, a little scientific, it is possible to experiment with electronic components already used in the industry for the generation of cooling and / or heating, acquiring Some Peltier cells and elaborating a small domestic system.
There has been a lot of talk about air conditioning, with important elements of an electromechanical system such as the compressor, fan motors, pipes and coils, refrigerant gas, all with a high economic cost in addition to the effects of energy consumption and the effects of leaks of polluting gases in some cases, but this time we want to go a step further and make a small design already used in car cellars and in some designs to small scale.
We know that we have already been evaluating larger-scale alternatives of models of much more cooling and / or heating capacity, in this sense we want to give an example of the construction of a simple system of low energy consumption with few elements for its manufacture, here we present a Peltier cell to be used as an air conditioning system.

Peltier cell
This type of cell works by the Peltier effect, which is based on the fact that when a current is passed through two metals or semiconductors joined by two "Peltier joints", a heat transfer is created from one joint to the other, causing as a result that one cools and another is heated. It would be something like a low-cost mini heat pump, without compressor, refrigerant or other complicated elements, simply a union between two materials.
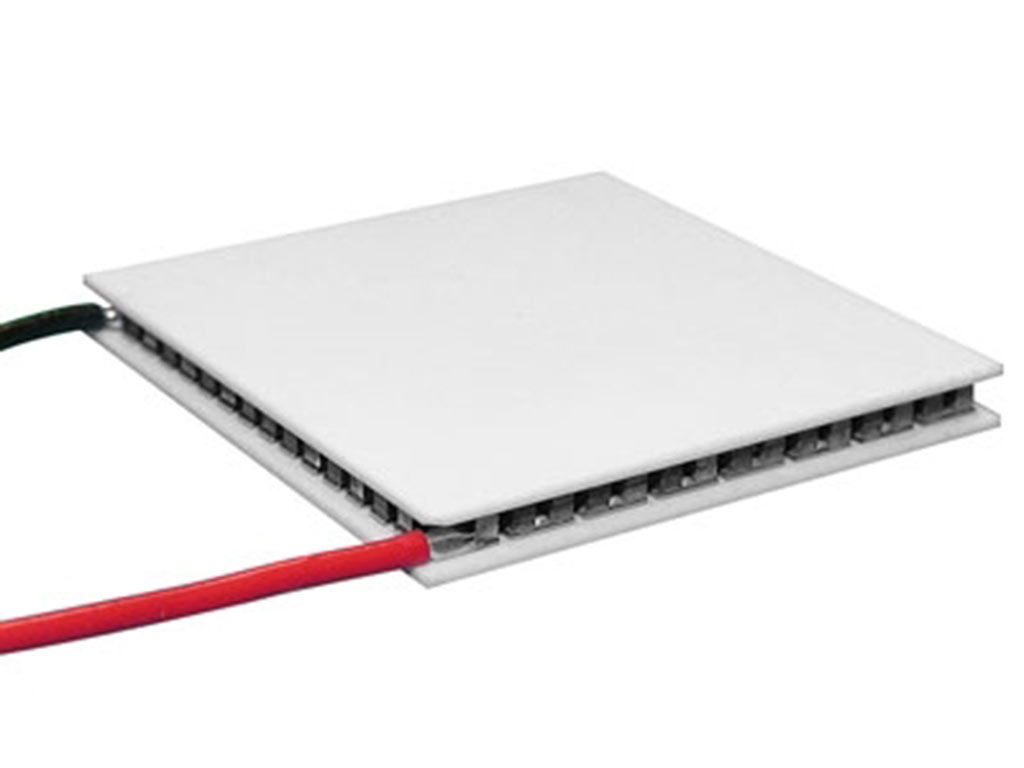

As a single junction does not produce hardly any power, Peltier cells consist of a multitude of junctions between two plates (usually 4×4 cm). Although you can not expect one of these plates to cool a barrel of beer much less.
This effect is used by some bottle racks that are used to maintain a moderate temperature inside and also some car refrigerators and similar systems.
Example of an air conditioning system
We are going to make a small model of what would be an air conditioner with this Peltier Cell the following basic components:
• Two PC microprocessor-type heatsinks with built-in fan
• A 12V and 8.5A power supply
• The TEC1-12706 peltier cell that can be purchased in a physical electronics store. Other materials: thermal paste, cables and some insulation.
The scheme of the assembly would be as follows:
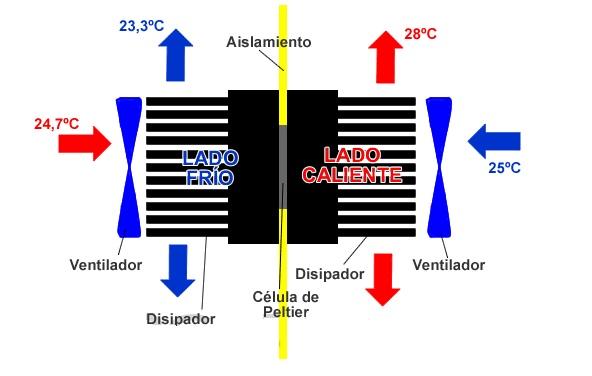
It is simply a heatsink-Peltier-heatsink assembly. It is necessary that both sides of the Peltier cell make good contact with the surface of the heatsinks, so we will use thermal paste and tighten a lot (blessed flanges!).
In addition, as the heatsinks are somewhat larger than the cell, we have filled this area with insulating material, here you can use almost any type of material that is not thermal conductive.
Although the assembly could be greatly improved, we have managed to lower the temperature at which the air takes almost 1.5ºC (from 24.7ºC to 23.3ºC), while the one that heats it does about 3ºC (from 25ºC to 28ºC).
In a test that we have done by installing the cold side inside a container and leaving the hot side on the outside, we have managed to maintain the temperature of the container above 22ºC while outside we were about 25ºC.
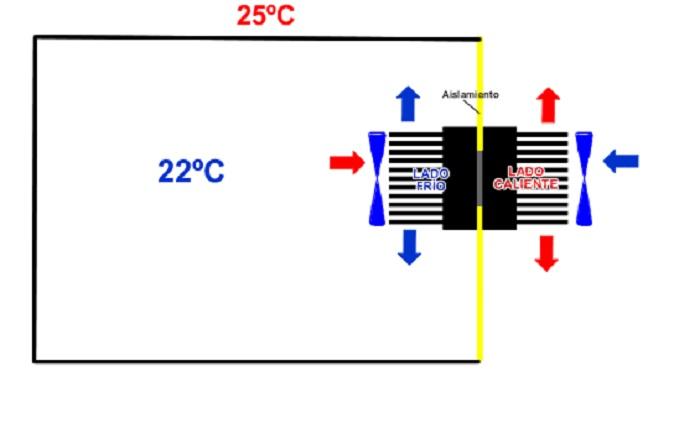
Obviously to make an air conditioner for a room with this system you will need many cells, or a very large cell that is not marketed as such at the moment at the level of electronic stores. To get an idea, we have made an estimate of the cooling power generated by the "mini air conditioning" and is approximately 15W, while the electricity consumption exceeds 40W, so it is not a very efficient system, but following the evaluation and experimentation you can achieve with few things a system that has no polluting elements, it does not require pipes, compressors and other more complex elements.
Another peculiarity that this small demonstration would have is that we can put it to work in "heat pump" or heating simply by changing the polarity in the power supply, in this way it would heat the container and cool the outside air.
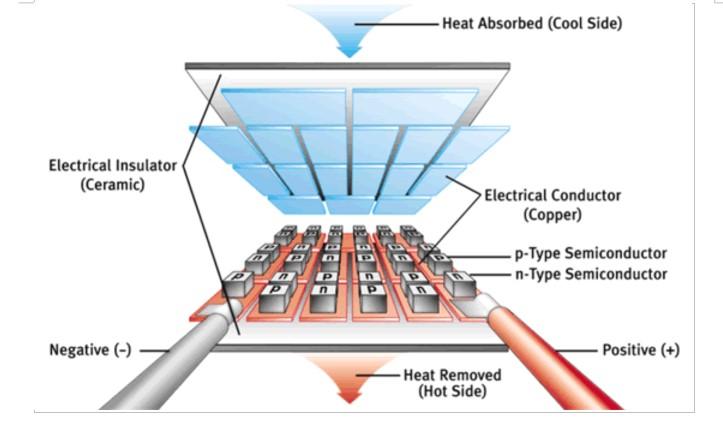
As an important point you should not connect the cell to the 12V, without making this assembly, that you know, that without dissipation of the heat generated, although one face cools with respect to the other, we will be able to put in less than 20 seconds the hot face at 150ºC and the "cold" one at 100ºC, and as a consequence the Peltier cell will burn.
With this small design we only want to present an alternative to some systems that, despite offering limited capacity, are being used and marketed, but that surely, in one way or another, are already being experimented and built larger and that provide a larger cooling and / or heating capacity.
 * Jimy Danelli is an air conditioning and refrigeration maintenance consultant. You can write to the email: [email protected]
* Jimy Danelli is an air conditioning and refrigeration maintenance consultant. You can write to the email: [email protected]















