International. The Korea Energy Research Institute has developed a new concept of refrigeration and freezing technology that uses air as a refrigerant, replacing conventional high-GWP refrigerants.
Researchers have successfully developed an ultra-high-speed integrated compression and expansion system, which combines a compressor and an expander, using advanced design technology. - The system is capable of cooling down to -100 degrees Celsius, so it is expected to have wide applications in semiconductor processes, biotechnology, pharmaceutical storage, and more.
The Korea Energy Research Institute (KIER) has developed, for the first time in the country, a refrigeration technology that uses air as a refrigerant instead of freon gas, hydrofluorocarbons (HFCs) and other refrigerants that cause global warming.
In March this year, the European Union's new regulations on fluorinated greenhouse gases (F-gases) came into force. From 2025, sales of products containing F-gases will be phased out. In addition, it is expected that the rules on processes using F-gases will be strengthened. Since F-gases are used in Korea's key export products, such as air conditioners, automobiles, and semiconductor processes, there is an urgent need to develop alternative technologies.
The research team successfully developed an integrated ultra-high-speed compressor-expander that is used in air cooling, and for the first time in Korea, created an air cooling system. With this system, it is possible to reach an ambient temperature of -60 degrees Celsius using air as a refrigerant.
Traditional refrigeration and cooling systems have mainly used the vapor compression cycle. In this method, cooling is achieved as the liquid refrigerant evaporates and absorbs heat. Due to its simple structure and design, it is widely used in various fields. However, a key drawback is their reliance on fluorinated greenhouse gases as refrigerants, which generates the impact of global warming.
In response to this, the research team focused on implementing a refrigeration system based on the reverse Brayton cycle, which uses air as a refrigerant. Unlike the traditional method that involves evaporating a liquid, this system compresses a gas and then goes through heat exchange and expansion to produce a gas at a low temperature, allowing cooling without the need for liquid refrigerants. However, the complexity of designing and building such a system has been a major challenge, preventing its application in refrigeration systems until now. The expander must be designed with extreme precision due to the ultra-fast speed rotation during the cooling process. For example, the gaps between the components and the shaft offset require a tolerance of 0.1 millimeters.
The reverse Brayton cycle works as follows:
- Compression: The air is compressed at high temperature and high pressure.
- Heat exchange: Compressed air passes through a heat exchanger, where it is cooled to a low temperature while maintaining high pressure.
- Expansion: Cooled and high-pressure air then expands in an expander, reducing it to a low temperature and pressure.
- Cooling: The cooled air is sent to the required area for cooling.
- This cycle is repeated to continuously supply cooled air for desired cooling applications.
To implement the reverse Brayton cycle system, the research team designed a compressor-expander system that connects the compressor, expander, and motor on a single shaft. Although the compressor and expander are connected to a single shaft, each device must operate at its own maximum efficiency. In addition, the shaft system design ensures stable operation even at ultra-high rotational speeds, further improving the reliability and performance of the system.
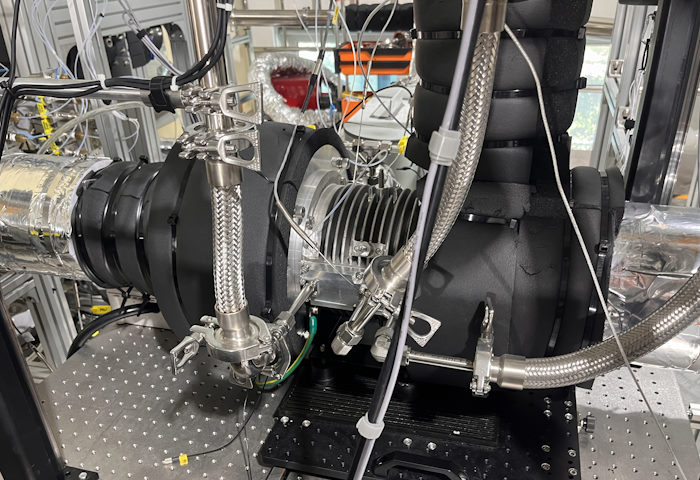
The refrigeration system using the developed compressor-expander managed to cool the air to less than -60 degrees Celsius in just one hour. Notably, by generating cold temperatures below -50 degrees Celsius, the system demonstrated higher cooling efficiency compared to traditional vapor compression systems. In theory, it is capable of cooling down to -100 degrees Celsius, and at that temperature, cooling efficiency is expected to improve by more than 50% compared to vapor compression systems.
Dr. Beom Joon Lee, the lead researcher, stated, "Due to environmental regulations, refrigeration systems that primarily use refrigerants with a high global warming potential are rapidly transitioning to the use of eco-friendly refrigerants." He added: "We are currently working to improve the performance of the system to enable the production of cold temperatures below -100 degrees Celsius. We envision this technology being applied in fields that require ultra-low temperatures, such as semiconductor processes, pharmaceuticals, and biotechnology."
a high global warming potential are rapidly transitioning to the use of eco-friendly refrigerants." He added: "We are currently working to improve the performance of the system to enable the production of cold temperatures below -100 degrees Celsius. We envision this technology being applied in fields that require ultra-low temperatures, such as semiconductor processes, pharmaceuticals, and biotechnology."
Meanwhile, this research was carried out with the support of the Ministry of Science and ICT's "Climate Change Response Technology Development Project" (led by Dr. Beom Joon Lee) and the basic research program of the Korean Energy Research Institute (led by Dr. Hyung-ki Shin).















