 To select a thermal insulation as a solution to different problems we must consider many variants that we will see below.
To select a thermal insulation as a solution to different problems we must consider many variants that we will see below.
by Arcadio Velásquez*
For several decades elastomers have been a thermal insulation material widely used globally, in projects of great importance and high value due to its multiple properties superior to traditional methods of thermal insulation. It is estimated that by 2024 the revenues resulting from this solution will be greater than 3 trillion US dollars worldwide (projections considered post-COVID-19 pandemic).
To select a thermal insulation as a solution to different problems, we must consider many variants, such as of course the thermal properties (thermal conductivity mainly), the flexibility of the material that facilitates the installation in a certain way, its mechanical resistance, the wide range of applications and its life expectancy.
Currently there is a considerable number of manufacturers in different countries, each with its own formulation, which makes one brand different from another, however, in some regions controlling the quality and characteristics of the material is a challenge, due to the different perspectives of each region and their respective regulations.
In that case, organizations and associations such as the American Society for Testing and Materials (ASTM) are responsible for developing standards to ensure that manufacturers follow the laws or regulations valid in each region.
ASTM developed the ASTM C534 standard – Standard specification for flexible elastomeric cell thermal insulation preformed in sheet and tubular form – and many countries, consultants and specialists have adopted this specification to ensure that products used in the given region meet rigorous quality specifications and meet needs.
This standard specifies the most relevant characteristics of elastomers used in the thermal insulation industry, such as thermal properties, physical properties, applications, water vapor resistance properties, finishing processes and quality assurance.
Classification
ASTM C534 covers cellular elastomers that are used as thermal insulation, which are manufactured in two forms, tubular and sheet:
• Type I: elastomers manufactured in a tubular way.
• Type II: elastomers manufactured in the form of sheet.
Additionally, they are classified according to their operating temperature, which defines their application:
• Grade 1: from -183 to 104°C [-297 to 220°F], for commercial use (including residential) and also flexible.
• Grade 2: from -183 to 175°C [-297 to 350°F], for industrial use considered flexible at high temperatures.
• Grade 3: from -183 to 120°C [-297 to 250°F], for industrial use without halogens added to the insulation and also flexible.
Terminology
According to this standard, manufacturers must declare their own terminology, following the following description: a cellular elastomer for thermal insulation and is defined as a foam of closed cellular structure (closed cell) made from natural or synthetic rubber, or a mixture of both, and that additionally contains other polymers or other chemicals or simply the mixture of both, and that it can be modified with other organic or inorganic additives added.
This foam has properties and characteristics similar to those of vulcanized rubber, with the ability to convert from a thermoplastic to a thermo-hardenable state by cross-linking (vulcanization) and that can also have the ability to substantially recover its original shape when tensioned or elongated.
The most common trade name given to this material is NBR (Nitrile Rubber Butadiene). However, in some countries they are known by the name of a specific brand, a very common practice in our Latin American countries. In the Middle East, for example, it is known as Rubber Insulation.
Life
Elastomers are thermo-hardenable and are not thermoplastic by nature and are expanded with foaming agents that decompose with the application of heat and these gases do not change over time, therefore the thermal conductivity of the insulation remains stable over time, hence part of the life expectancy of the material, however, there are other characteristics that contribute to improving the life expectancy of the material, for example they must have a uniform core density and have closed cells, the latter contributes to the improvement of the resistance to the passage of water vapor. (extensive description in the qualitative requirements).
Physical characteristics
Qualitative Requirements: The ASTM C534 standard defines some physical and qualitative characteristics that manufacturers of such materials should consider, including:
• Thermal conductivity: when tested at an average temperature of 24 ⁰C this must be equal to or less than:
◦ 0.040 W/mK for Grade 1 and 3, Type I and II.
◦ 0.043 W/mK for Grade 2, Type I and II.
• Water Absorption: this must be equal to or less than:
◦ 0.20% by volume. For both types and all grades.
• Permeability of water vapor: this must be equal to or less than:
◦ 1.44 × 10-10 g/Pa·s·m For both types and all grades.
• Linear contraction at its maximum temperature of use: must be equal to or less than:
◦ Linear change 7% For both types and all grades.
The content of closed cells is a very relevant physical characteristic, since it determines the empty spaces that can be occupied by water molecules either by the transmission of water vapor or the absorption of water, both parameters will be judged according to the content of closed cells.
If the content is low, the risk of water accumulation in the insulating core becomes greater, as time goes by the water accumulates considerably affecting the thermal conductivity, so this standard is very rigorous to guarantee users a material with a long life expectancy.
The physical characteristics detailed above are essential to determine the useful life of the material, there is a wide and strong relationship between them, especially between thermal properties and properties to resistance to the passage of water vapor. In the graph below we can see how the thermal conductivity of an insulating material manufactured with different physical characteristics (properties of resistance to the passage of water vapor) varies, this variation is due to the fact that the core of each sample has different content of closed cells.
The sample represented by the blue curve contains more closed cells at its core when compared to the sample represented by the orange curve, allowing the material to have a more stable thermal conductivity over a period of 25 years and therefore a stable thermal performance with a longer life expectancy.
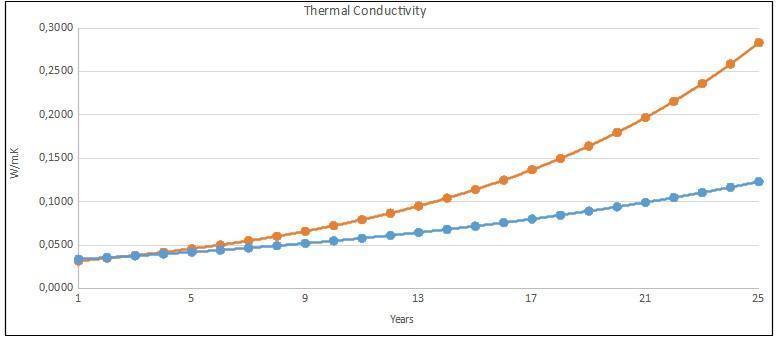
Figure 1.
In the following image we can see a clear example of a material that does not meet the physical characteristics of thermal properties, content of closed cells and resistance to the passage of water vapor, this can generate what is known as (or as I personally call), a reaction
in chain that begins with a condensation product of the impoverished resistance to the passage of water vapor, accumulation of water, then growth of fungi and development of microorganisms and this in turn leads to the deterioration of air quality and the affectation of nearby systems (example, oxidation of metal elements).
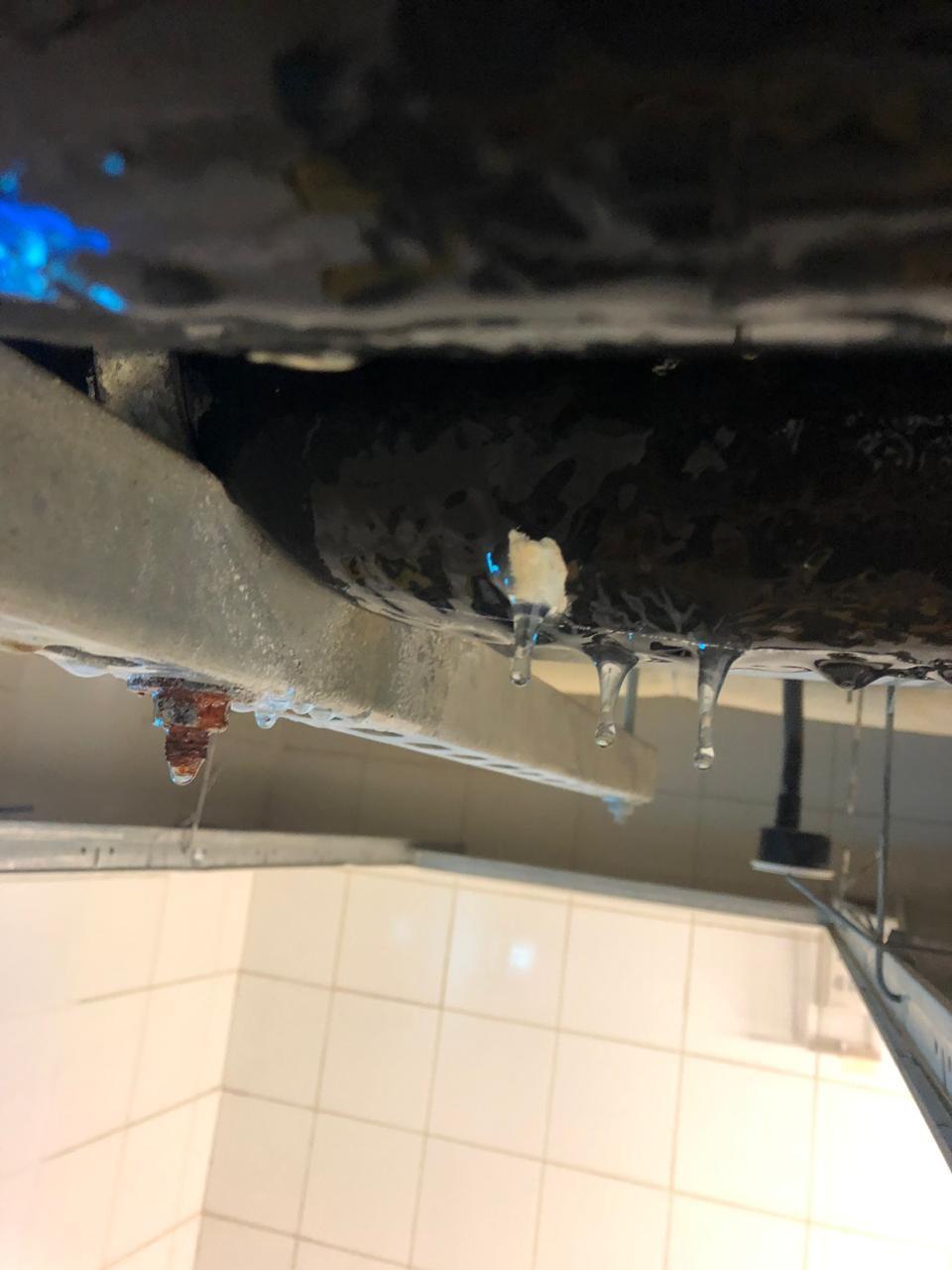

Image 1.
- Requirements for Inspection: in order to ensure quality, there are some requirements demanded by the standard that complement the inspection to place on the market a product that is in line with the specifications of the projects.
The first thing is to make sure that the material meets the aforementioned physical characteristics; then, it is important that the appearance of the material is free of visual defects that negatively affect the quality of the service. For example, bubbles or tears. In addition, it must be free of emission of unpleasant odors when subjected to the aforementioned design working temperatures.
In addition to quality control, this standard includes the specification of acceptable tolerances, mentioned below based on standard measures:
Board
As for fire behavior, a very important characteristic associated with the construction material, including thermal insulation of pipes and ducts, we must consider that ASTM C534 includes one of the most rigorous fire tests, the ASTM E84, which determines the combustion characteristics of the surface. In that case, the optimal results are those capable of maintaining a flame propagation index equal to or less than 25 and a developed smoke index equal to or less than 50. It should be noted that this test method does not always define the potential hazard of elastomeric cellular thermal insulation in real fire conditions. This is an organic material and is combustible therefore should not be exposed to flames or other sources of ignition.
Other considerations
Most elastomers used as thermal insulation contain halogens, however, there is a specific application that requires a limited use of halogens, this is because halogens can react when in contact with austenite, a component used in stainless steel pipes, this reaction causes corrosion on stainless steel.
In this case, it is required to study the materials through a chemical analysis determined by the ASTM C871 method, this quantifies the presence of chlorides and / or leachable fluorides, to classify the material as safe or not to be used on stainless steel with high austenite content, we must refer the results to the Acceptability graph of the insulation material based on the trace points of the analysis of Cl and (Na + SiO3) described in ASTM method C795.
This specification standard requires that the material be manufactured with the minimum quality requirements, therefore, many manufacturers strive to exceed these requirements to stand out in the markets and position their products among the most viable options, an interesting number of standards or test methods are required to comply with the ASTM C534 specification. Among them are: (I will name the most common, however, there are many options in the specification, all ASTM) Thermal conductivity, C518; water vapor permeability, E96; temperature range C411; water absorption, C209; chemical analysis, C871; fire behavior, E84; Density, D1622; range of measurements and tolerances, C585.
For more information, I recommend that you read with determination the original ASTM C534 standard.
 * Arcadio J. Velásquez | Mechanical Engineer . Mr. Technical Marketing Engineer – Hira Industries LLC Dubai, UAE. [email protected]
* Arcadio J. Velásquez | Mechanical Engineer . Mr. Technical Marketing Engineer – Hira Industries LLC Dubai, UAE. [email protected]














