This article aims to explain fundamental concepts to perform a component analysis in a refrigeration system and obtain choices that favor a lower consumption of equipment.
This article aims to explain fundamental concepts to perform a component analysis in a refrigeration system and obtain choices that favor a lower consumption of equipment.
By Juan Pablo Cárdenas*
As a consequence of not performing analyses in refrigeration systems, it is unknown to have a load balance against capacity; this dramatically affects the energy efficiency of the system and directly influences the useful life of the components involved, due to very large capacities, high pressures in condensation, overheating of the compressors, among others.
To understand and perform comprehensive efficiency assessment in a refrigeration system, concepts such as the following must be understood:
Temperature change.
Pressure delta.
Enthalpy delta.
Compression.
Expansion, among others.
These elements are part of the cooling system, for this it is necessary to make a thermodynamic summary evaluating the cooling system.
The cooling cycle is designed so that through the evaporation of a refrigerant liquid, heat is extracted from an enclosure or chamber, by means of radiators or coils which make the transfer of heat from the environment to be cooled and the refrigerant gas that circulates through the coil pipe.
When the refrigerant leaves this stage it will be in a gaseous state that a compressor needs to raise the pressure and temperature, which will expel it towards the radiator or condenser coil that will make a heat transfer with the environment, so that the transfer is made the refrigerant must have a temperature higher than that of the environment.
By expelling much of the heat into the environment and after condensing, the system requires a device which performs a pressure drop of the liquid and an expansion before entering the evaporator coil again.
The cooling capacity (QB) is the heat adsorbed in the evaporated coil and the cooling charge is the thermal energy presented by the load.
Compressor work (W) refers to the difference between dissipated heat (QA) and adsorbed heat (QB).
These above values can be estimated with the enthalpy change that is performed in the system stages.
QB= m (hs-he) evaporator
QA=m (he-hs) capacitor
W=m (hs-he) compressor
m : mass flow
h : enthalpies
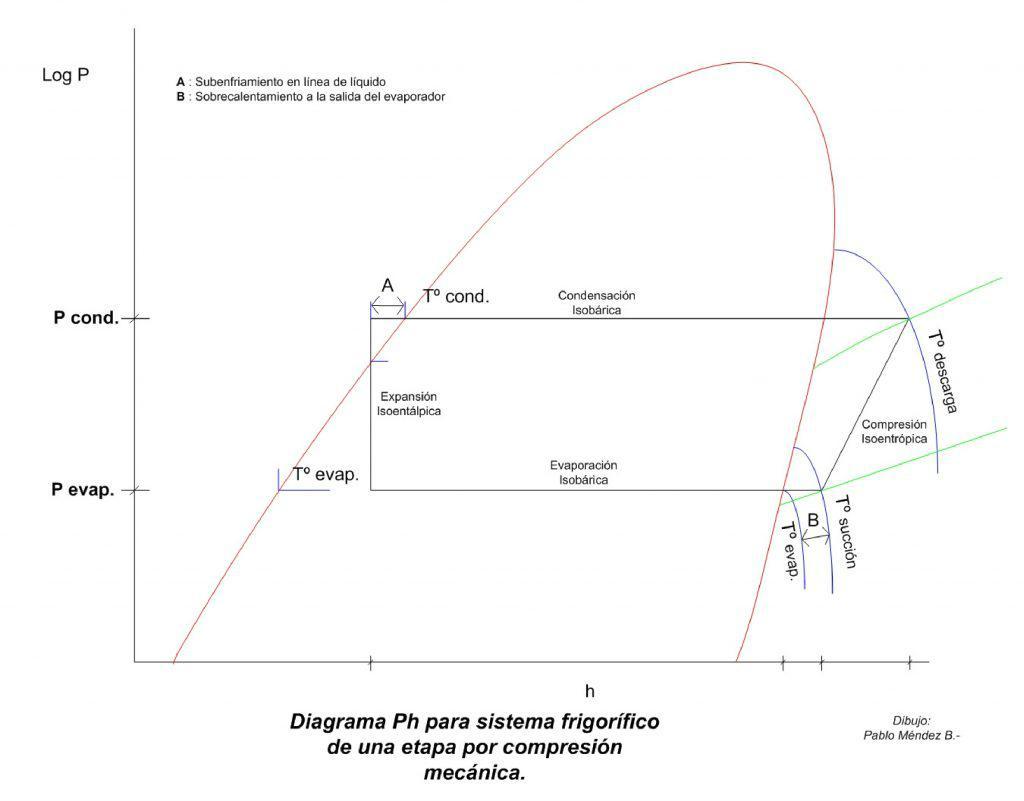
Figure 1.
The actual cooling cycles have losses, which make the real not equal to the calculated, some losses will be seen below.
- Compression is not adiabatic.
- Condensation and evaporation processes are not isobaric due to frictional pressure losses.
- There is a sub cooling of liquid before the TX and an overheating upon arrival of the compressor.
Efficiencies
To find efficiency, the following terms must be spoken of:
COP: Operating coefficient
COP = QB/W = (he-hs) evaporator / (hs-he) compressor
It is the ratio between the heating power and the electrical power absorbed under specific temperature conditions with the unit at full load. Heating mode
EER: Energy efficiency ratio
EER= (QB, BTU/h) / Watt
It is the ratio between the cooling power and the electrical power absorbed under specific temperature conditions with the unit at full load. Cooling mode
SEER: Seasonal energy efficiency ratio
SEER=(QB, BTU/year) / Watt-h
It is the seasonal energy efficiency of a unit, calculated for the annual demand for cooling, seasonal energy efficiency factor
PAE: Percentage of evaporator utilization
PAE=x/l
L: evaporator length
X: distance where evaporation occurs
It is the percentage of use of the evaporator, it is a measure of the efficiency achieved in the use of the evaporator.
All these results can be found theoretically or ideally and in a real way. To achieve real development of these values, main measurements must be taken in the cooling system such as pressure and temperature at the following points:
Compressor suction, compressor discharge, condenser inlet, condenser outlet, expansion valve inlet, expansion valve outlet, evaporator inlet, evaporator outlet.
A source of opportunity of the present is to carry out projects with operating and energy efficiencies as high as possible, but even more the development of new technologies in the facilities already installed that do not have systems that help energy efficiency.
Regulate evaporation capacity
Some systems already installed have equipment (compressors) robust in capacity compared to the current loads they require, meaning the evaporation pressures that work are much lower than those required by the system to meet the need, causing excessive work of the equipment, thus increasing energy consumption.
For this there are regulation systems in the compressors that are responsible for varying the capacity so that it consumes less electrical power by lowering its RPM as the variator, or digital regulation systems in the compressor such as digital dischargers.
Condensation regulation
In the same way as in the previous example in large part the facilities of the past do not present regulation in the capacity of condensation, that is to say in hours of the day the equipment can use 100% of its load due to the ambient temperature, but at night due to the decrease in the ambient temperature, the condenser becomes more efficient or with a much larger capacity, however, it continues to work the engines 100% as if it were going to supply the total load, that is where the opportunity for improvement comes in. The speed of the capacitor motors can also be regulated or a stage control can be installed to turn off some motors, which has an impact on lower energy consumption.
According to the above, at present it is sought to guarantee a high efficiency of the equipment in terms of its capacity regulation to generate that the equipment has a much higher energy efficiency.
This situation is solved with a very good calculation of thermal loads considering their application and all the variables that affect the design, with the aim of generating a balance in the cooling system, supported by other elements for the control of suction and condensation pressures such as variable speed drives, dischargers, electronic expansion valves, sub cooling of liquid lines among others.
* Juan Pablo Cárdenas, Director of Engineering Industries Refridcol.