 We present an interesting case of integration of the air conditioning system with the refrigeration system carried out in a supermarket.
We present an interesting case of integration of the air conditioning system with the refrigeration system carried out in a supermarket.
by Eng. Ernesto Sanguinetti R. – Eng. José Lescano D.- COLD IMPORT S.A. – Lima - PERU*
Initially the markets had self-contained refrigeration equipment in each refrigerated cabinet where perishable food products were displayed and sold to the public. Having the equipment self-contained means that the complete equipment is part of the furniture and that the heat that evacuates the condenser is delivered directly to the environment of the place where the public makes the purchases.
Later with the increase in the population and the demand for food appear supermarkets and hypermarkets with the consequent increase in the dimensions and the amount of refrigerated furniture. The use of refrigerated furniture with self-contained equipment had to be ruled out because the heat evacuated by each condenser would significantly influence the thermal load of the furniture or furniture itself and the comfort of customers when raising the temperature of the premises.
The most logical thing was chosen: that each refrigerated cabinet maintains its Evaporator or Evaporator Unit and its Thermostatic Expansion Valve inside each piece of furniture but that the Condensation Unit formed by the compressor and the condenser are installed in a machine room outside the premises, making the connection between them by copper pipes. That engine room could be located on a first floor or a second floor but outside the sales premises, which made the condensers better ventilated and that the heat they evacuate goes directly to the outside atmosphere.
Large pipe lengths and a greater amount of cooling fluid began to be used, but the expressed advantages were achieved. To store larger quantities and replenish what was sold in the refrigerated furniture of the stores, cold rooms and also process rooms in the back rooms began to be used. Always with your own complete cooling equipment: Evaporator Unit or evaporator inside the chamber and Condensation Unit in the Engine Room.
For many years a Condensation Unit was used for each refrigerated cabinet and cold room, thus having a large number of Condensation Units in the engine rooms.
With the passage of time, several problems were observed:
-When the humidity of the environment inside the sales premises or store was high, all refrigerated furniture inevitably had to extract moisture from the environment, so those above 0°C had to drain a large amount of condensed water (they had to remove additional sensitive heat) and those that were at 0°C and less froze the moisture on the evaporator coils (I had to remove additional sensitive heat) an to remove sensitive heat and additional latent heat) which in turn caused increased de-icing cycles. In both cases there was a higher energy consumption to maintain each design condition because the thermal load of each piece of furniture had to be added to the thermal load to condense and / or freeze the humidity of the ambient air of the store.
- Condensation was also observed on the surfaces of the refrigerated furniture and that the water droplets that were formed presented an unpleasant appearance to the eye, then when sliding and reaching the floors near each piece of furniture they showed a "wet" floor also with an unpleasant appearance but with the aggravating factor of being an imminent danger that they can slip and / or fall customers or employees of the establishment, in addition, the appearance of bad odors under the furniture and premature oxidation of metal surfaces were detected.
-Additionally, it was observed that the glass roofs and doors were fogged with the condensation of moisture, layers of ice were formed on the surface of the frozen products or on their wrapping or packaging. Another aspect not pleasant to the eye and touch of customers.
All of the above prompted the search for a solution and the best solution was to install air conditioning systems to condition the air of the entire commercial premises because with this two things are achieved:
-Control the temperature and humidity of the air to minimize and, if possible, avoid the problems mentioned above.
-Provide customers with a pleasant atmosphere whose permanence to these conditions is instinctively longer (especially in summer) and invites to make more purchases.
Soon it became necessary to analyze the consumption of electrical energy in a supermarket finding that the distribution was approximately the following (see graph 1):
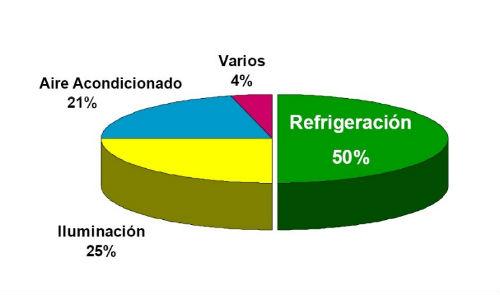
Figure 1.
Installation of compressors in parallel
Once the previous analysis was carried out, we entered the stage of seeking the improvement of energy consumption to lower these percentages or to optimize consumption. The stage of eliminating the Condensing Units for each refrigerated piece of furniture was entered. Instead of several Condensation Units, compressors began to be installed in parallel, divided into medium temperature compressors that is called "medium temperature group" (for furniture and cold rooms for the conservation of fresh products) and in low temperature compressors that is called "low temperature group" (for furniture and conservation chambers of frozen products).
This set of compressors in parallel began to be called "compressor rack" that were mounted on a single metal structure or chassis that is located in a smaller engine room and that all discharged into a single air-cooled condenser that is installed on the roof of the Supermarket or Hypermarket.
With the use of compressors in parallel, the efficiency of the food refrigeration system in supermarkets was improved, because by modulating its operation we achieved that the demand of the system adjusts to the refrigeration demand, for which strategies were applied using compressors with dischargers, then variable speed drives and digital compressors. Hand in hand with these technologies was the development of electronic controllers that allowed to apply operating logics achieving significant energy savings.
Integration
As mentioned, in a supermarket refrigeration and air conditioning systems account for approximately 70% of total electrical energy consumption, this leads us to continuously look for improved systems. One option is to integrate the air conditioning system with the refrigeration system and this can be achieved by developing the following designs:
1. A plant with a rack of compressors that have a single discharge to a condenser but have three independent "suction temperature groups": Air Conditioning, Medium Temperature and Low Temperature.
Advantages: Lower installation and operation cost because we centralize refrigeration and air conditioning systems in an engine room.
Disadvantages: Having a common discharge means using a single refrigerant for all three suction groups. R134a refrigerant can be used for high and medium temperature groups, however, it is not efficient to use it for low temperature group. On the contrary, if we use R449 or R507 they have good performance in low temperature, but not so in high and medium temperature.
2. Have the air conditioning system separate and independent (Central Air Conditioning with compressors in parallel) and take advantage of the refrigerant liquid of its circuit to sub-cool the refrigerant liquid of the "medium and low temperature group" of the refrigeration system (Food Cold Center), or if we have an air conditioning system with "ice water", we can take advantage of the water, also to sub-cool the coolant of the food cold system. In graph 2 you can see schematically both systems:
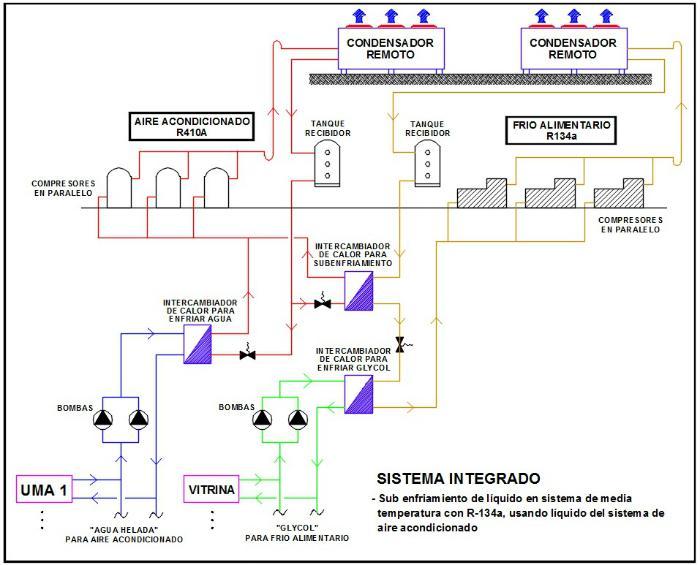
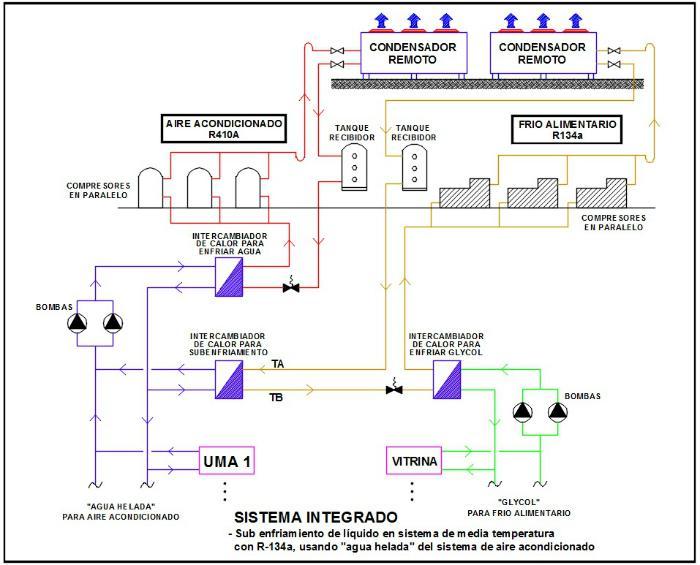
Advantages:
- We take advantage of the air conditioning system that has a higher evaporation temperature to sub-cool the refrigerant liquid of the refrigeration system with which we increase the cooling capacity (we improve the refrigerant effect in the thermodynamic cycle) with which the compressors perform less work and this allows us to select compressors of lower capacity.
- The COP performance coefficient of the refrigeration system is improved since energy savings are achieved by consuming less electrical energy to drive the compressors.
- By having coolant that reaches the expansion valve at a lower temperature, we also manage to reduce its size.
- Lower installation and operation cost since both plants will be located in the same engine room. Reducing spaces, we achieve greater ease and access for assistance to the systems (preventive maintenance, corrective maintenance).
Disadvantages:
- At night in supermarkets they turn off the air conditioning equipment and if the system is integrated, the food cold will not be harmed as long as the compressor center in parallel has variable speed drives or another digital device to ensure the refrigeration demand.
- The heat rejected in the exchanger by the coolant of the refrigeration system is absorbed by the air conditioning system. Therefore, it is very important to determine the optimum point of liquid sub-cooling (TA – TB in the graph above) since we can increase the energy consumption in the air conditioning system too much.
By determining the optimum point of subcooling we ensure an energy advantage in the integrated system (refrigeration and air conditioning), which will depend on the condensation temperatures considered in each installation site.
In Lima - PERU in 2016 an integrated system was installed in a supermarket of approximately 4,500 m2, achieving good results. We are developing similar projects to be installed now in 2017.
* Engineers Ernesto Sanguinetti R. and José Lescano are part of the company Cold Import S.A. of Lima – Peru. They can be contacted at [email protected] emails or [email protected]














